- +27 79 866 5061
solutions@resatech.co.za
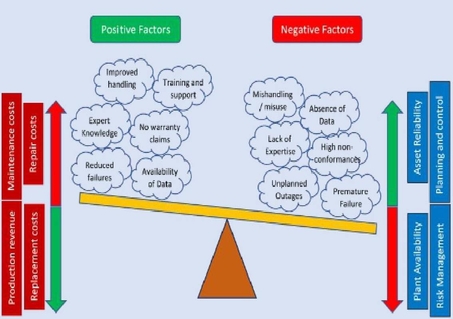
Rotating electrical machines are among the most complex and expensive items in the modern power plant. Their purchasing and reconditioning account to a large portion of the capital investment for the plants. Their reliability is however hampered by high number of inexplicable failures which often result in exorbitant cost of repair and replacement in addition to loss of enormous production revenue. Curbing these failures calls for an in-depth study of various failure modes and their implications as observed from each asset individually. The absence of relevant historical data pertaining to the actual operational details of the machine while in service as well as the unavailability of data trends relating to other variables which have direct influence on the overall machine performance make it difficult, if not impossible to administer appropriate counter measures in an effort to restrain the upsurge in premature failures and minimise the overall lifecycle costs of rotating electrical machines.

The necessary material required to develop effective maintenance programs to better safeguard these assets is often available and quite easily accessible however, it needs to be constantly collected, systematically organised, well managed and meticulously analysed to provide the evidence required and augment the calls for intensified continuous improvement initiatives. Contrary to popular belief, the installation of insulation health monitoring systems does not prevent failure of rotating machines but provides critical information regarding the health of the insulation system in time to enable power plant and asset managers to better plan for condition-based maintenance. A couple of questions need to be answered to develop an airtight program to reduce lifecycle costs of rotating machines.
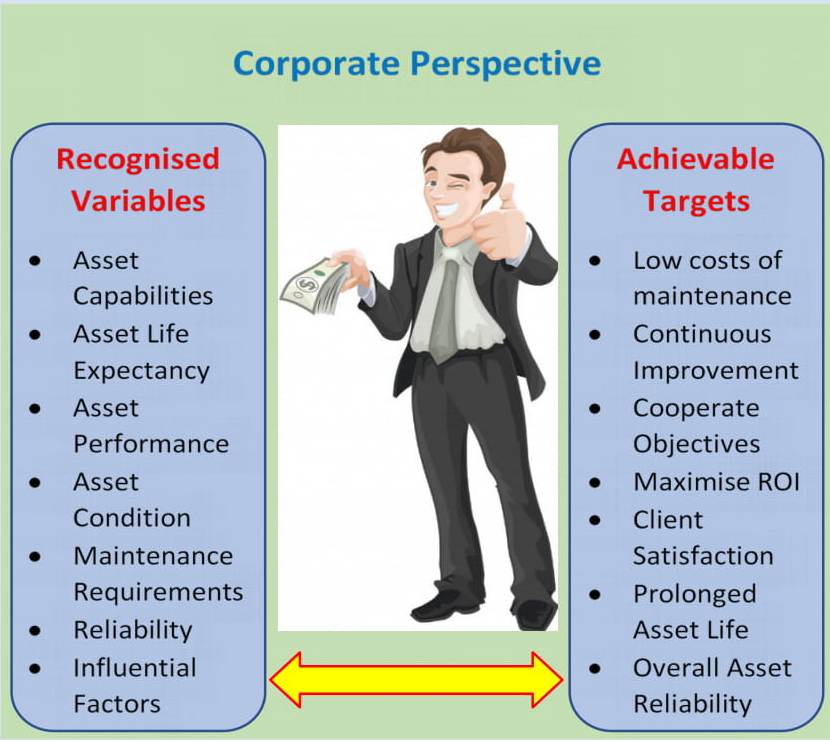
Operational excellence is every executive decision-maker’s desire in every industrial establishment across the globe. Realizing efficiencies depends on the alignment of needs and requirements with the existing capabilities and resources. Therefore, a complete understanding of medium voltage assets, their capabilities, lifecycle, performance, condition assessment, maintenance requirements, reliability, external factors and their influence on the asset’s operation, etc. should be easily accessible to key role players so that questions relating to operational efficiencies could be answered.
These critical aspects are fully encompassed in our innovative asset management strategy to facilitate a smooth process of ensuring continuous improvement, achievement of corporate objectives and maximization of return on investment in the most cost-effective manner possible. Our Smart Asset Reliability Program (SARP) is designed to help modern industrial power plant owners better identify risks and determine needs for optimization while achieving their projected targets in the smartest manner possible.